Tag: #otd
18 December 1941 – today in history…
by Volker on Dec.18, 2025, under Allgemein
After the failed missions in August and September 1940, the Decima MAS returned to the eastern Mediterranean in order to make another attemp to attack the Harbour of Alexandria with SLC devices of the Mezzi d’Assalto: “Operazione G.A.3”, carried out by Tenente di Vascello Luigi Durand de la Penne and Capo Palombaro I Emilio Bianchi (SLC 221), Capitano Genio Navale Antonio Marceglia and Sottocapo Palombaro Spartaco Schergat (SLC 222), Capitano Armi Navale Vincenzo Martellotta and Sottocapo Palombaro Mario Marino (SLC 223).
 What turned out to be one of the most famous SLC missions in the Second World War has been announced in the Italian War Bulletin N. 585 of the 8th of January 1942: “On the night of the 18th December assault craft of the Italian Royal Navy entered the Harbour of Alexandria and attacked two British battleships anchored there. It has only just been confirmed that a battleship of the Valiant class was seriously damaged and put into dock for repairs, and is still there.”
What turned out to be one of the most famous SLC missions in the Second World War has been announced in the Italian War Bulletin N. 585 of the 8th of January 1942: “On the night of the 18th December assault craft of the Italian Royal Navy entered the Harbour of Alexandria and attacked two British battleships anchored there. It has only just been confirmed that a battleship of the Valiant class was seriously damaged and put into dock for repairs, and is still there.”
Bulletin N. 586 of the 9th of January 1942, added the following: “In the Operation conducted by assault craft fo the Royal Italian Navy in the Harbour of Alexandria and reported in yesterday’s Bulletin we now have definite further intelligence that, in Addition to the Valiant, a second battleship of the Barham class was also damaged.”
 Winston Churchill announced in a speech before a secret session of the House of Commons on the 23rd of April 1942: “A further sinister stroke was to come. On the early morning of December 19 half a dozen Italians in unusual diving suits were captured floundering about in the Harbour of Alexandria… Four hours later explosions occurred in the bottoms of the Valiant and the Queen Elizabeth, produced by limpet bombs fixed with extra-ordinary courage and ingenuity, the effect which was to blow large holes in the bottoms of both ships and to flood several compartments, thus putting them both out of Actions for many months…”
Winston Churchill announced in a speech before a secret session of the House of Commons on the 23rd of April 1942: “A further sinister stroke was to come. On the early morning of December 19 half a dozen Italians in unusual diving suits were captured floundering about in the Harbour of Alexandria… Four hours later explosions occurred in the bottoms of the Valiant and the Queen Elizabeth, produced by limpet bombs fixed with extra-ordinary courage and ingenuity, the effect which was to blow large holes in the bottoms of both ships and to flood several compartments, thus putting them both out of Actions for many months…”
Read chapter II.I of our book “The References” 1930’s-1940’s to find out what happened on 18 December 1941 (page 118-125). More on the historic content in our “The References” book set with a total of 1392 pages can be found here and here. You can purchase “The References” 1930’s-1940’s in our bookstore. Enjoy reading!
18 November 1944 – today in history…
by Volker on Nov.18, 2025, under Allgemein
 Read chapter VII of our book “History2” to find out what happened on 18 November 1944. Rare documents helped us to capture the history behind a Ref. 3646 / Type D “Kampfschwimmer” watch, which can be found in this chapter.
Read chapter VII of our book “History2” to find out what happened on 18 November 1944. Rare documents helped us to capture the history behind a Ref. 3646 / Type D “Kampfschwimmer” watch, which can be found in this chapter.
Beside photos from the years 1944 and 1945 showing the watch on the frogman’s wrist, as well as his identification papers and travel documents issued in Venice (see photo), helped us to reconstruct the route Hanns-Martin Kaufhold took to the mission grounds in the last months of the Second World War.
Read more about chapter VII of “History2” (70 pages, 58 photos, 6 technical illustrations) here. and here. You can purchase your copy of “History2” in our bookstore.
30 September 1940 – today in history…
by Volker on Sep.30, 2025, under Allgemein
 The afternoon of 30 September 1940 marks the end of the mission „Operazione G.A.2“. Just five weeks after the sinking of the Iride, the Gondar (photo: historic crest of the submarine, showing SLC containers on its deck) was the second transport submarine of the Mezzi d’Assalto to be sunk.
The afternoon of 30 September 1940 marks the end of the mission „Operazione G.A.2“. Just five weeks after the sinking of the Iride, the Gondar (photo: historic crest of the submarine, showing SLC containers on its deck) was the second transport submarine of the Mezzi d’Assalto to be sunk.
The submarine Gondar (built in 1937) under the command of Tenente di Vascello Francesco Brunetti was dispatched from La Spezia with Alexandria as her target. On board the Gondar was the officer-in-charge of mission G.A.2, Mario Giorgini, three SLC teams and a reserve team.
When the Gondar reached the target area on 29 September 1940, she received a sobering radio message from reconnaissance: The British fleet had left the Port of Alexandria – so mission G.A.2 was aborted. The Gondar headed now for Tobruk and was already on its return journey when it was discovered by the Australian destroyer, HMAS Stuart. A second destroyer, HMS Diamond and a corvette now tracked the Gondar throughout the night alongside HMAS Stuart.
 After hours of attempting to evade capture, the Gondar gave up in the early hours of 30 September 1940. Commander Brunetti gave the order to dive down and abandon the Gondar, which effectively saved his team and the SLC pilots from going down after being sunk by the mighty enemy. A British Sunderland flying boat bombarded the Gondar while the crew was already in the water – effectively sealing the fate of the second transport submersible for SLCs (see historic photos on the left). For one of the two inventors of the new weapon, Elios Toschi, this second journey was also to be his last. He was taken prisoner by the British alongside the crew of the Gondar and his comrades – “missione fallita”.
After hours of attempting to evade capture, the Gondar gave up in the early hours of 30 September 1940. Commander Brunetti gave the order to dive down and abandon the Gondar, which effectively saved his team and the SLC pilots from going down after being sunk by the mighty enemy. A British Sunderland flying boat bombarded the Gondar while the crew was already in the water – effectively sealing the fate of the second transport submersible for SLCs (see historic photos on the left). For one of the two inventors of the new weapon, Elios Toschi, this second journey was also to be his last. He was taken prisoner by the British alongside the crew of the Gondar and his comrades – “missione fallita”.
The launch of the new weapon appeared to be ill-fated: Two operations (G.A.1 and G.A.2) failed, two valuable transport submersibles had been sunk and four SLC teams and their officers-in-charge had been taken as prisoners of war. It was to take over a year until another attempt could be made to penetrate the Port of Alexandria in December 1941…
Read more about “The birth of a legend – the first Panerai watches (1935-1939)” in chapter I on page 34-39, followed by the timeline of the missions during the Second World War in chapter II.I on page 106-109. Mario Giorgini, officer-in-charge of the mission G.A.2 is also featured in the second volume of “The References” on page 1016-1022. The Gondar is also featured in our book “History1” in chapter IV on page 288-357.
21 August 1940 – today in history…
by Volker on Aug.21, 2025, under Allgemein
 Gulf of Bomba (Lybia). In August 1940, the time had finally come to put the new SLC weapon to the test. Alexandria in the eastern Mediterranean was the main base of the British Mediterranean fleet. The battleships at anchor there were the first targets for missions of the Mezzi d’Assalto involving the SLCs.
Gulf of Bomba (Lybia). In August 1940, the time had finally come to put the new SLC weapon to the test. Alexandria in the eastern Mediterranean was the main base of the British Mediterranean fleet. The battleships at anchor there were the first targets for missions of the Mezzi d’Assalto involving the SLCs.
The transport submersible Iride, under the command of Tenente di Vascello Francesco Brunetti, prepared for its tour of duty with the SLCs on 21 August 1940, ready to attack the Port of Alexandria in the night of 25/26 August 1940. Eleven servicemen with four SLCs aboard the torpedo boat Calipso were dispatched to the Gulf of Bomba on the Libyan coast. There, the SLCs were tested at held ready for departure until they were ready to launch mission G.A.1 a few days later with the submersible Iride.
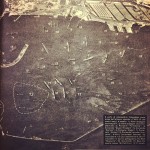
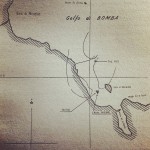 Right at the start of its test run, however, the submersible Iride was spotted by three Fairey Swordfish torpedo bombers, which had launched from the aircraft carrier HMS Eagle. The enemy bombers began their attack straight away (see historic map on the left).
Right at the start of its test run, however, the submersible Iride was spotted by three Fairey Swordfish torpedo bombers, which had launched from the aircraft carrier HMS Eagle. The enemy bombers began their attack straight away (see historic map on the left).
The shallow water in the Gulf of Bomba prevented the Iride from descending quickly. Instead, it attempted to ward off the attack at full speed with its anti-aircraft cannons. At the same time, Brunetti tried in vain to direct the bow of the submersible towards the attackers in order to reduce the area of the Iride exposed to attack. However, the Iride was soon hit by a torpedo and sank. The boats quickly dispatched to the scene managed to rescue some of the shipwrecked crew members from the Iride. A dramatic race against time began.
 The SLC teams under Gino Birindelli (right in the photo), Teseo Tesei, Elios Toschi, Luigi Durand de la Penne and Emilio Bianchi dived straight down to the wreck of the Iride in order to save the survivors who were trapped down there. Although the equipment belonging to the SLC pilots on board the Iride was lost, but the three SLCs were recovered for use in later missions. The SLCs pilots returned to the Bocca di Serchio on board the Calipso.
The SLC teams under Gino Birindelli (right in the photo), Teseo Tesei, Elios Toschi, Luigi Durand de la Penne and Emilio Bianchi dived straight down to the wreck of the Iride in order to save the survivors who were trapped down there. Although the equipment belonging to the SLC pilots on board the Iride was lost, but the three SLCs were recovered for use in later missions. The SLCs pilots returned to the Bocca di Serchio on board the Calipso.
During the rescue of the survivors from the Iride, they had pushed themselves to the very limit of what was humanly possible. Loss of human life and equipment was the sobering result of the first mission „Operazione G.A.1“ with the new weapon of the Mezzi d’Assalto.
Read more on Gino Birindelli, one of the surviving SLC teams, in chapter VIII.II on page 1014-1043 or click also here. More information on the historic content in our “The References” book set can be found here. Read about the featured watches from Guido Panerai & Figlio in the first and second volume here.
25 July 1941 – today in history…
by Volker on Jul.25, 2025, under Allgemein
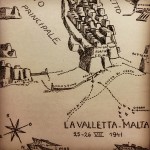 Augusta (Sicily) 11 pm. The night of 25 July 1941 marks the beginning of the “Operazione Malta 1”, known by its disastrous result for the Mezzi d’Assalto, only three months after the first successful attack with MT explosive boats against British ships in Souda Bay (Crete) on 26 March 1941. One day later, in the early morning of 26 July 1941, the Decima MAS lost the head of the flotilla (Capitano di Fregata Vittorio Moccagatta), the head of explosive boats (Capitano di Corvetta Giorgio Giobbe), the doctor of the flotilla (Tenente Medico Bruno Falcomatà), SLC pilots (including their inventor, Teseo Tesei) and MT explosive boats pilots during the attack of the harbour of La Valetta (Malta).
Augusta (Sicily) 11 pm. The night of 25 July 1941 marks the beginning of the “Operazione Malta 1”, known by its disastrous result for the Mezzi d’Assalto, only three months after the first successful attack with MT explosive boats against British ships in Souda Bay (Crete) on 26 March 1941. One day later, in the early morning of 26 July 1941, the Decima MAS lost the head of the flotilla (Capitano di Fregata Vittorio Moccagatta), the head of explosive boats (Capitano di Corvetta Giorgio Giobbe), the doctor of the flotilla (Tenente Medico Bruno Falcomatà), SLC pilots (including their inventor, Teseo Tesei) and MT explosive boats pilots during the attack of the harbour of La Valetta (Malta).
 On a side note of the history, the commander of the explosive boats / “Mezzi di Superficie”, Giorgio Giobbe (1906-1941), is well known for wearing his Panerai watch on his right wrist in a photo taken prior the mission against Malta (see page 111-115 in chapter II.I). More about missions and watches of the Decima MAS can be found here.
On a side note of the history, the commander of the explosive boats / “Mezzi di Superficie”, Giorgio Giobbe (1906-1941), is well known for wearing his Panerai watch on his right wrist in a photo taken prior the mission against Malta (see page 111-115 in chapter II.I). More about missions and watches of the Decima MAS can be found here.
Read more about “The birth of a legend – the first Panerai watches (1935-1939)” in chapter I, followed by the timeline of the missions during the Second World War in chapter II.I – more information on the historic content in our “The References” book set can be found here. Read about the featured watches from Guido Panerai & Figlio in the first and second volume here.
30 October 1940 – today in history…
by Volker on Oct.30, 2024, under Allgemein
1940. The first mission against the Port of Gibraltar (B.G.1) was aborted when it became clear that the British fleet had already left for Operation “Menace”. The transport submersible Scirè under the command of Junio Valerio Borghese was still 50 nautical miles off Gibraltar. Disappointed, the SLC teams returned to their secret base at Bocca di Serchio, where they intensively discussed the feasibility of this type of attack. This happened at the same time when „Operazione G.A.2“ was about to end with the sinking of the transport submersible Gondar.
 Initial, decisive proof of the feasibility and the successful, secret penetration of enemy ports was achieved by Comandante Borghese and his men in mission B.G.2. Again, three SLCs were dispatched: Teseo Tesei with Alcide Pedretti, Luigi Durand de la Penne with Emilio Bianchi and Gino Birindelli with Damos Paccagnini.
Initial, decisive proof of the feasibility and the successful, secret penetration of enemy ports was achieved by Comandante Borghese and his men in mission B.G.2. Again, three SLCs were dispatched: Teseo Tesei with Alcide Pedretti, Luigi Durand de la Penne with Emilio Bianchi and Gino Birindelli with Damos Paccagnini.
The Scirè came into position at around 1.30 a.m. on 30 October 1940 in order to allow the SLC teams to disembark from the conning tower of the submersible. The Scirè only remained at the surface for a short time so that the three SLC teams could reach the cylindrical pods on the deck of the submersible. The Scirè then retreated back beneath the surface. Under water, the three teams manoeuvred their SLCs out from the pods and started their attack on the Port of Gibraltar. The three teams experienced problems almost as soon as the attack began. While Tesei and his co-pilot Pedretti had problems with their breathing apparatus, Durand de la Penne and his co-pilot Bianchi experienced problems with their electric engine. Both teams decided to abort the attack and sink their SLCs. However, only De la Penne managed to do this. Tesei’s SLC was washed up on the Spanish coast near La Linea and caused quite a stir among both the Spanish authorities and the British secret service. Both teams swam to the Spanish coast and were able to return safely to Italy with the help of the Italian secret service.
 The fate of the entire operation now lay in the hands of Gino Birindelli and his co-pilot Damos Paccagnini. Unaware of the fact that their comrades-in-arms had already had to terminate their mission, they launched their attack on the Port of Gibraltar. Although mission B.G.2 was in principle a failure because not one enemy ship was sunk, Birindelli and his co-pilot Paccagnini were able to prove for the first time that a “maiale” was able to enter an enemy port unnoticed.
The fate of the entire operation now lay in the hands of Gino Birindelli and his co-pilot Damos Paccagnini. Unaware of the fact that their comrades-in-arms had already had to terminate their mission, they launched their attack on the Port of Gibraltar. Although mission B.G.2 was in principle a failure because not one enemy ship was sunk, Birindelli and his co-pilot Paccagnini were able to prove for the first time that a “maiale” was able to enter an enemy port unnoticed.
„Operazione B.G.2“ marked the start of a three year war that took place noiselessly and under water in the Bay of Gibraltar. For Gino Birindelli, however, the mission marked the start of a journey through Allied POW camps that would last many months. Read more on mission B.G.2 and the story of Gino Birindelli in our book “The References” 1950’s-1960’s in chapter VIII.II on page 1014-1043.
26 May 1941 – today in history…
by Volker on May.26, 2019, under Allgemein
 In May 1941, the Decima MAS continued its attacks on the Port of Gibraltar. This time, the SLC pilots’ energy was preserved because they were flown over to Spain disguised as crew members and shipping company employees so that they wouldn’t have to go through the lengthy approach by submarine. Once they had arrived in Spain, they travelled overground to the Port of Cádiz, where the Italian tanker Fulgor had been detained since Italy joined the war.
In May 1941, the Decima MAS continued its attacks on the Port of Gibraltar. This time, the SLC pilots’ energy was preserved because they were flown over to Spain disguised as crew members and shipping company employees so that they wouldn’t have to go through the lengthy approach by submarine. Once they had arrived in Spain, they travelled overground to the Port of Cádiz, where the Italian tanker Fulgor had been detained since Italy joined the war.
On 15 May 1941, the transport submarine Scirè left the Port of La Spezia with the “maiali” on board, but without their pilots. After passing the Strait of Gibraltar on 22/23 May, Borghese reached the Port of Cádiz and overnight took on board the six SLC pilots who had previously been on the Fulgor: Decio Catalano and Giovanni Giannoni, Amedeo Vesco and Amelio Franchi (replaced by reserve Antonio Marceglia), Licio Visintini and Giovanni Magro.
 Despite the successful deployment of the three SLCs on 26 May 1941, the B.G.3 mission failed due to technical problems and a good deal of bad luck in the last phase of the attack when an explosive charge that had been successfully attached to the hull of a ship became detached at the last second. All six SLC pilots reached the Spanish coast and were able to return to their base at Bocca di Serchio with the aid of the Italian Consul in Algeciras.
Despite the successful deployment of the three SLCs on 26 May 1941, the B.G.3 mission failed due to technical problems and a good deal of bad luck in the last phase of the attack when an explosive charge that had been successfully attached to the hull of a ship became detached at the last second. All six SLC pilots reached the Spanish coast and were able to return to their base at Bocca di Serchio with the aid of the Italian Consul in Algeciras.
However, the mission B.G.3 still had some positive aspects: The British did not notice the operation and the element of surprise was not wasted. The use of the tanker Fulgor as a forward base on Spanish territory proved extremely useful and effective.